Internet Evolution: Tracing the Historical Milestones from ARPANET to Web 3.0
The Internet, the global system of interconnected networks that we are so dependent on today, has a fascinating history filled with innovation, collaboration, and revolution.
The story of the Internet is a testament to human ingenuity and the drive to create and connect.
This article will explore the history of the Internet, tracing its roots from its inception as a military project to its modern role as the backbone of global communication and commerce.
Table of Contents
The Birth of the Internet: ARPANET
In the late 1960s, the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was created by the U.S.
Department of Defense’s Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA, now DARPA).
ARPANET was the first wide-area packet-switching network with distributed control and one of the first networks to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite.
Both technologies became the technical foundation of the Internet.
The first ARPANET message was sent by UCLA student programmer Charley Kline on October 29, 1969, under the supervision of Professor Leonard Kleinrock.
The message was meant to be “LOGIN,” but the system crashed after just two letters, resulting in the first message being the rather less impressive— “LO”.
Evolution and Proliferation: From NCP to TCP/IP
The Network Control Protocol (NCP) was initially used as the core protocol in ARPANET. However, as the network expanded, the need for a more versatile and robust protocol was identified.
This led to the development of Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which was designed by Vinton Cerf and Robert E. Kahn.
TCP/IP was tested across the network on January 1, 1983, and became the standard networking protocol on ARPANET and, subsequently, the Internet.
The adoption of TCP/IP was like laying the Internet’s foundation: it allowed multiple networks, including ARPANET, to converge into a global network of networks.
The Birth of the World Wide Web
The concept of the World Wide Web was proposed in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee, a British computer scientist working at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research.
He envisioned it as a global information-sharing space, where people could access information from any point in the world.
Berners-Lee also created the first web browser, web server, and coding languages HTML (HyperText Markup Language), URI (Uniform Resource Identifier), and HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol), the foundational technologies for websites.
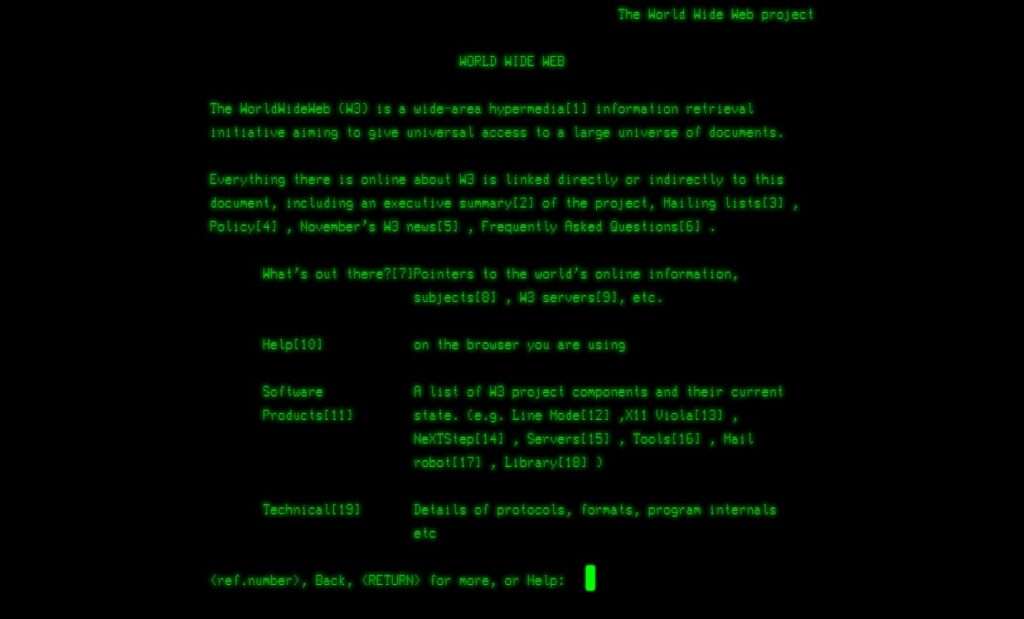
The first-ever website created by Tim Berners-Lee, went live at CERN in December 1990.
Which is still live today and can be visited at this URL: http://info.cern.ch/. It was put back online by CERN in 2013 as a historical document.
Rapid Expansion and the Dot-Com Bubble
The mid-90s saw the rapid commercial expansion of the Internet, often referred to as the Dot-Com Bubble. During this period, speculations drove the value of internet-based companies extraordinarily high.
Despite many of these companies lacking a profitable business model, their stock prices soared in this frothy stock market environment.
However, by 2001 the bubble burst, leading to a crash in the stock market and the bankruptcy of many internet-based businesses.
Despite this setback, the Internet was firmly entrenched in the public’s consciousness, and its use continued to grow exponentially.
The Social Internet: Web 2.0
Post the Dot-Com Bubble, the Internet evolved towards greater interactivity and user-generated content.
This phase, known as Web 2.0, saw the rise of social networking sites, blogs, wikis, and video sharing sites.
Giants like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter emerged during this period, changing the way people connect and share information.
The Future: Web 3.0 and Beyond
Today, we’re on the brink of another revolutionary phase in the Internet’s evolution, often referred to as Web 3.0 or the semantic web.
This phase represents an Internet that’s becoming more intelligent, with advancements in AI, machine learning, and data analytics leading the way.
Web 3.0 is expected to deliver personalized experiences tailored to individual users and enable more efficient data integration and connectivity.
Technologies like blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT) are also playing a significant role in this transformation, paving the way for a more secure, decentralized, and interconnected Internet.
Conclusion
The history of the Internet is a tale of continuous evolution and adaptation.
From ARPANET to the World Wide Web, from the Dot-Com Bubble to the rise of Web 2.0, the Internet has consistently shaped, and been shaped by, our world.
As we step into the era of Web 3.0, it remains to be seen how the Internet will continue to evolve and what new opportunities it will offer.
Remember, the Internet is not just a technology; it’s a platform for human connection, a tool for knowledge sharing, and a driver of economic growth.
As we look back at its history, we also look forward to the future, anticipating the innovations and transformations the Internet will bring.
FAQs
Q1: What is the Internet?
The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers that communicate with each other using standardized protocols. It provides a platform for sharing information, resources, and services across the world.
Q2: When was the Internet invented?
The concept of the Internet began in the 1960s, with the development of ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network), the first network to use the TCP/IP protocol suite, which laid the foundation for the modern Internet.
Q3: Who invented the Internet?
The Internet was not invented by a single individual. It evolved over time through the collaborative efforts of many researchers and scientists. Key contributors include Vinton Cerf, Bob Kahn, Tim Berners-Lee, and others.
Q4: What was the first website?
The first website, created by Tim Berners-Lee, went live on August 6, 1991. It was a basic text page explaining the World Wide Web project and how to create web pages.
Q5: What is the World Wide Web (WWW)?
The World Wide Web is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. It was proposed by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 and has become a crucial aspect of the Internet, enabling the creation and navigation of websites.
Q6: When did the Internet become publicly accessible?
The Internet became publicly accessible in the late 1980s and early 1990s as various networks and services opened up to the general public. The introduction of browsers like Mosaic and Netscape in the early 1990s made the Internet more user-friendly.
Q7: What is the significance of the dot-com boom?
The dot-com boom refers to the rapid growth of Internet-related businesses in the late 1990s. This period saw a surge in investment and the creation of many online startups, although it eventually led to the dot-com bust in the early 2000s.
Q8: How has the Internet evolved over the years?
The Internet has evolved from a text-based, academic network to a multimedia-rich, globally accessible platform. Advances in technology, the rise of social media, e-commerce, and the proliferation of mobile devices have shaped its ongoing evolution.
Q9: What is the role of government in the development of the Internet?
Initially, the development of the Internet was heavily funded and influenced by government agencies, such as the United States Department of Defense through ARPANET. However, over time, it transitioned to a more commercially driven and globally collaborative effort.
Q10: How has the Internet impacted society?
The Internet has profoundly impacted society by revolutionizing communication, commerce, education, and entertainment. It has connected people globally, facilitated the exchange of information, and transformed various aspects of daily life.



Comments